Inside Collagen: The Truth About Peptides and Aging
In recent years, collagen supplements have gained tremendous popularity in the health and beauty industries. At MDhair, we're constantly researching the most effective ingredients for hair, skin, and joint health. Collagen peptides stand out as one of the most scientifically supported supplements available today. But what exactly are they, and how do they work to improve your body's natural collagen production? This article explores the clinical evidence behind collagen peptides and their benefits for overall wellness.
Understanding Collagen: The Body's Structural Protein
Collagen constitutes approximately one-third of the total protein in the human body, making it the most abundant structural protein we have. Its primary role is to maintain the health and mechanical properties of connective tissues, including the skin, hair follicles, joints, and bones. As the principal component of the extracellular matrix (ECM), collagen is vital for strength, regulation, and regeneration of these tissues.
Characterized by its unique triple-helix structure, collagen contains high concentrations of three amino acids: glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. These amino acids create the distinctive structure that gives collagen its remarkable tensile strength and flexibility.
The Natural Decline of Collagen
Unfortunately, our body's natural collagen production begins to decline as early as our 20s, decreasing by approximately 1-1.5% per year. By age 40, most individuals have lost about 10-20% of their collagen stores, which explains many of the visible signs of aging:
- Fine lines and wrinkles
- Thinning hair
- Joint stiffness and discomfort
- Decreased skin elasticity
This decline makes supplementation an attractive option for those looking to support their body's collagen levels as they age.
What Are Collagen Peptides?
Collagen peptides (also called hydrolyzed collagen) are smaller, more bioavailable fragments of collagen that have been enzymatically broken down to enhance absorption in the digestive tract. Unlike intact collagen, these peptides can be easily absorbed into the bloodstream, where they can reach target tissues throughout the body.
The enzymatic hydrolysis process breaks down the collagen's triple-helix structure into shorter peptide chains that are more readily absorbed and utilized by the body. These collagen peptides don't possess the gelling properties of gelatin (another form of processed collagen) and are soluble in cold water, making them convenient for supplementation.
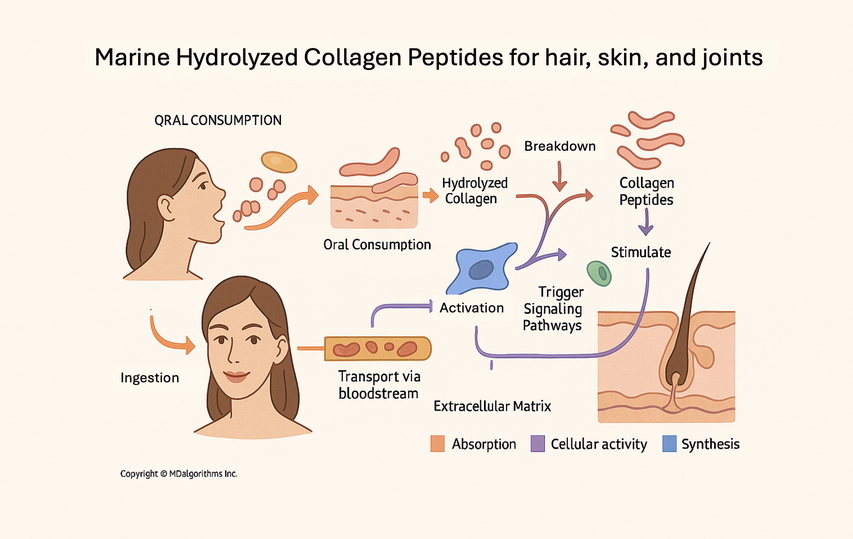
Clinical Evidence: How Collagen Peptides Work
The efficacy of collagen peptides isn't just marketing hype—it's backed by scientific research. Here's what the clinical studies tell us about how collagen peptides work in different areas of the body:
Skin Health Benefits
Collagen peptides have been shown to improve skin elasticity, hydration, and appearance. A systematic review of randomized controlled trials found that oral collagen supplementation improved skin hydration, elasticity, and dermal collagen density.
The mechanism works in two ways:
- Providing building blocks: The peptides deliver essential amino acids needed for collagen synthesis
- Signaling effects: The specific peptides act as messengers that stimulate fibroblasts (the cells responsible for collagen production) to produce more collagen, elastin, and hyaluronic acid
One study demonstrated that participants taking 2.5-5g of collagen peptides daily for 8 weeks showed significant improvements in skin elasticity compared to those taking a placebo. Another study found that women who took collagen supplements for 12 weeks experienced increased skin hydration and a significant reduction in wrinkle depth.
A meta-analysis published in the International Journal of Dermatology in 2021 concluded that 90 days of collagen supplementation can reduce wrinkles and improve skin hydration and elasticity.
A 2022 study with 100 participants showed that the oral supplementation of low-molecular-weight collagen could improve wrinkles, elasticity, hydration, and barrier integrity of photoaged facial skin without adverse effects.
Hair Strength and Growth
While direct studies on collagen for hair growth are more limited than those for skin, there's promising evidence that collagen peptides may support hair health by:
- Providing amino acids necessary for keratin production (the primary protein in hair)
- Supporting the health of the dermal layer where hair follicles are anchored
- Potentially fighting free radical damage to hair follicles
The amino acid profile of collagen-rich in proline, which is also a key component of keratin, makes it a complementary supplement for hair strength. Additionally, collagen's role in supporting proper blood circulation may help deliver nutrients to the hair follicles more efficiently.
Joint Health and Cartilage Regeneration
The scientific evidence for collagen's benefits on joint health is particularly robust. Collagen peptides have been shown to have a positive impact on joint pain and functionality, especially when combined with exercise.
A 24-week study involving athletes with activity-related joint pain found that those taking 10g of collagen hydrolysate daily experienced significant reductions in joint pain during rest, walking, standing, and carrying objects. The collagen group also required fewer alternative therapies to manage their pain compared to the placebo group.
Another study using 5g of collagen peptides daily for 12 weeks demonstrated a more pronounced reduction in knee pain compared to placebo (38.4% vs. 27.9% reduction). The researchers proposed several mechanisms for these benefits:
- Increased synthesis of type I, II, and IV collagen in articular cartilage
- Enhanced production of proteoglycan and elastin
- Formation of extracellular matrix molecules, leading to increased firmness of connective tissue
- Anti-inflammatory properties, with glycine potentially inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokine release
Optimal Dosing and Timing
Research indicates that different doses of collagen may be appropriate depending on your health goals:
- For Hair & skin benefits: 2.5-5g daily
- For joint health: 5-10g daily
Interestingly, studies on collagen synthesis have discovered that timing matters. When taking collagen before exercise, the peptides appear to be more effectively incorporated into tissues. One study found that taking 15g of collagen peptides enriched with vitamin C approximately 60 minutes before exercise led to a significant increase in collagen synthesis markers.
Vitamin C plays a crucial role in this process through its involvement in the hydroxylation of proline and lysine, both essential for creating the collagen helix formation and intermolecular cross-linking. This explains why many quality collagen supplements include vitamin C in their formulations.
Marine Collagen: The Premium Option for Hair, Skin, and Joints
While collagen peptides can be sourced from bovine, porcine, and poultry sources, marine collagen (derived from fish) offers several distinct advantages:
Superior Bioavailability
Marine collagen peptides are typically smaller in size than those derived from land animals, resulting in better absorption and bioavailability. This means the beneficial compounds can more efficiently reach the dermis layer of the skin, hair follicles, and joint tissues.
Environmentally Sustainable
The marine collagen in MDhair products is sourced using sustainable practices, utilizing parts of fish that would otherwise be discarded. This makes it an environmentally responsible choice compared to some other collagen sources.
Type I Collagen Rich
Marine collagen is predominantly Type I collagen—the most abundant collagen type in human skin, hair, nails, organs, bones, and ligaments. This makes it particularly effective for cosmetic and dermatological applications.
Hypoallergenic Profile
For those with sensitivities to bovine or porcine products, marine collagen presents a hypoallergenic alternative with a lower risk of allergic reactions or religious/dietary restrictions.
Clinical Evidence: MDhair Marine Collagen's Impact on Hair Structure
MDhair's clinical research has demonstrated marine collagen's effectiveness for hair health. In a recent six-month clinical study published in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology (March 2025), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) revealed remarkable improvements in hair texture and structure in participants using MDhair's personalized regimens that included marine collagen peptides.
The study observed that hair strands showed "normalization of cuticle structure and reduced hair shaft damage after 24 weeks of treatment," with participants experiencing a reduction in hair damage by one to two grades on the standard SEM hair health grading scale. Before treatment, many participants' hair exhibited irregular cuticle patterns with poorly defined scale surfaces, often resembling a "melted candle" appearance. After six months of treatment with marine collagen and other customized products, SEM images documented significant improvements in the hair shaft surface texture, resulting in stronger, more resilient hair.
MDhair Marine Collagen: Formulated for Total Body Wellness
MDhair's Marine Collagen is specifically formulated to support not just hair health, but also skin elasticity and joint function. Our formula contains optimally sized peptides for maximum absorption, along with synergistic ingredients like hyaluronic acid and vitamin C to enhance collagen's effectiveness.
Unlike generic collagen supplements, our formula is:
- Derived from wild-caught marine sources
- Enzymatically processed for optimal bioavailability
- Third-party tested for purity and potency
- Free from artificial additives and preservatives
- Formulated with complementary nutrients that enhance collagen synthesis
Regular users of MDhair Marine Collagen report improvements in hair thickness and growth, and noticeable benefits in skin texture and joint comfort—a true whole-body approach to collagen supplementation.
Conclusion: The Science-Backed Approach to Collagen Supplementation
The research is clear: collagen peptides offer significant benefits for skin, hair, and joint health when taken consistently at appropriate doses. The mechanisms through which they work—providing essential building blocks and signaling cellular activity—are well-documented in scientific literature.
By choosing a high-quality marine collagen supplement like MDhair's, you're investing in a scientifically supported approach to maintaining the structural integrity of your body's tissues as you age. Whether you're concerned about thinning hair, skin elasticity, or joint discomfort, collagen peptides represent one of the most comprehensively researched natural approaches to supporting your body's own collagen production.
References
- Bhardwaj V, Rodgers N, Harth O, Harth Y. Artificial Intelligence-Based Personalization of Treatment Regimen for Hair Loss: A 6-Month Clinical Trial. J Drugs Dermatol. 2025 Mar;24(3):233.
- Khatri, M., Naughton, R. J., Clifford, T., Harper, L. D., & Corr, L. (2021). The effects of collagen peptide supplementation on body composition, collagen synthesis, and recovery from joint injury and exercise: a systematic review. Amino Acids, 53(10), 1493-1506.
- Clark, K. L., Sebastianelli, W., Flechsenhar, K. R., Aukermann, D. F., Meza, F., Millard, R. L., & Albert, A. (2008). 24-Week study on the use of collagen hydrolysate as a dietary supplement in athletes with activity-related joint pain. Current Medical Research and Opinion, 24(5), 1485-1496.
- Zdzieblik, D., Oesser, S., Gollhofer, A., & König, D. (2017). Improvement of activity-related knee joint discomfort following supplementation of specific collagen peptides. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, 42(6), 588-595.
- Shaw, G., Lee-Barthel, A., Ross, M. L., Wang, B., & Baar, K. (2017). Vitamin C-enriched gelatin supplementation before intermittent activity augments collagen synthesis. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 105(1), 136-143.
- Asserin, J., Lati, E., Shioya, T., & Prawitt, J. (2015). The effect of oral collagen peptide supplementation on skin moisture and the dermal collagen network: evidence from an ex vivo model and randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 14(4), 291-301.
- Proksch, E., Segger, D., Degwert, J., Schunck, M., Zague, V., & Oesser, S. (2014). Oral supplementation of specific collagen peptides has beneficial effects on human skin physiology: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology, 27(1), 47-55.
- León-López, A., Morales-Peñaloza, A., Martínez-Juárez, V. M., Vargas-Torres, A., Zeugolis, D. I., & Aguirre-Álvarez, G. (2019). Hydrolyzed collagen—sources and applications. Molecules, 24(22), 4031.
- Praet, S. F. E., Purdam, C. R., Welvaert, M., Vlahovich, N., Lovell, G., Burke, L. M., & Waddington, G. (2019). Oral supplementation of specific collagen peptides combined with calf-strengthening exercises enhances function and reduces pain in Achilles tendinopathy patients. Nutrients, 11(1), 76.
- Choi, F. D., Sung, C. T., Juhasz, M. L., & Mesinkovsk, N. A. (2019). Oral collagen supplementation: A systematic review of dermatological applications. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology, 18(1), 9-16.
- Sibilla, S., Godfrey, M., Brewer, S., Budh-Raja, A., & Genovese, L. (2015). An overview of the beneficial effects of hydrolysed collagen as a nutraceutical on skin properties: Scientific background and clinical studies. The Open Nutraceuticals Journal, 8(1), 29-42.
Find the most effective hair growth products for you by taking the free hair assessment.




